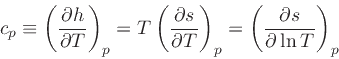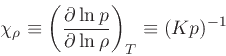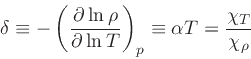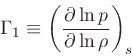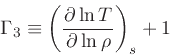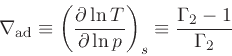



Next: 2.3.3 CO5BOLD equation of
Up: 2.3 A collection of
Previous: 2.3.1 Basic thermodynamic equations
Contents
Index
Definition of specific heats:
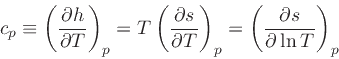 |
(27) |
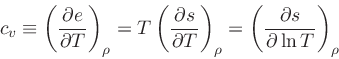 |
(28) |
Definitions of further thermodynamic coefficients:
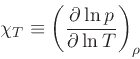 |
(29) |
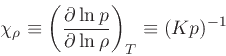 |
(30) |
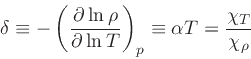 |
(31) |
It can be shown that
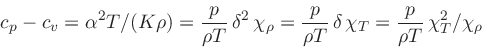 |
(32) |
Definition of adiabatic exponents:
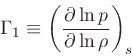 |
(33) |
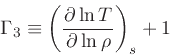 |
(34) |
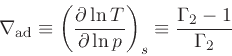 |
(35) |




Next: 2.3.3 CO5BOLD equation of
Up: 2.3 A collection of
Previous: 2.3.1 Basic thermodynamic equations
Contents
Index