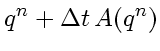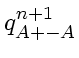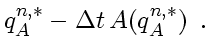



Suppose both operators
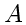 and
and
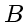 are zero,
are zero,
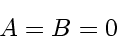 |
(214) |
resulting in individually
stationary solutions
(eg. hydrostatic and radiative equilibrium),
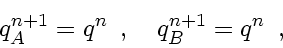 |
(215) |
which gives for both operator combination methods
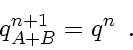 |
(216) |
However, if the individual operators are non-zero but cancel each other,
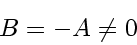 |
(217) |
the adding of the operator gives equilibrium Eq. (216),
while operator splitting
This is not necessarily a stationary solution.
Here, operator adding is superior.
![]() and
and
![]() are zero,
are zero,