



Next: 7.1.22 Scale and test
Up: 7.1 Parameter file: rhd.par
Previous: 7.1.20 Time-step control
Contents
Index
Subsections
7.1.21 Input/output control
With this group of parameters
the start model and the type and amount of output can be specified.
Parameters with the suffix ``_start'' describe the initial model,
these with suffix ``_end'' the corresponding final model.
Additional data can be written
into the file described by the parameters with suffix ``_full''
(full 2D/3D model dumps, huge, see Sect.8.1)
or
into the file described by the parameters with suffix ``_mean''
(additional information, see Sect.8.3).
The interval between datasets in the full file can be set e.g. with
real dtime_out_full f=E15.8 b=4 n='Output time step' u=s &
c0='dtime_out_full < 0.0 => no output' &
c1='dtime_out_full = 0.0 => output every time step'
2.0E+06
Allowed values are
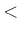
0.0: No output to this file
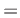
0.0: Output at every time step. Attention: This can produce HUGE files in no time.

0.0: Output to full file approximately every dtime_out_full seconds.
Some examples: The ``classical'' value for this output for simulations of solar granulation
is 20sec.
To save memory this can be increased to 30sec.
But in this case chromospheric shocks are very badly resolved.
To cover them properly, a sampling rate of 10sec or below is needed.
On the other hand, if no good time resolution is needed a sampling rate of
a few minutes might be sufficient.
7.1.21.2 real dtime_out_end
The interval between outputs into the end file can be set e.g. with
real dtime_out_end f=E15.8 b=4 n='Output time step' u=s &
c0='dtime_out_end < 0.0 => output only at very end' &
c1='dtime_out_end = 0.0 => output every time step' &
c2='dtime_out_end > 0.0 => output every dtime_out_end seconds (and at end)'
1.0E+04
Allowed values are
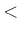
0.0: Output only at very end of run (classical behavior).
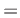
0.0: Output at every time step.
Attention: This can produce lots of I/O operations and can take a long time.
However, it will not produce a large file.
Instead, the end file is written over and over again.

0.0: Output to end file approximately every dtime_out_end seconds
(and at the very end of the simulation).
The standard value is -1.0, not enabling any additional output into this file.
A value a reasonable factor smaller than real dtime_out_full seems appropriate.
The interval between datasets in the mean file can be set e.g. with
real dtime_out_mean f=E15.8 b=4 n='Output time step' u=s &
c0='dtime_out_mean<0.0 => no output'
0.5E+06
Allowed values are
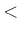
0.0: No output to this file
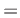
0.0: Output at every time step.

0.0: Output to mean file approximately every dtime_out_mean seconds.
Because the size of one mean dataset is much smaller than one full dataset,
it is possible to request a higher sampling rate without using too much disk space.
7.1.21.4 integer n_outslicedim_mean
The index of the optional slice in the mean output file can be specified with e.g.
integer n_outslicedim_mean f=I4 b=4 n='index of slice in mean output file' u=1 &
c0='0: no output of slice' &
c1='1, 2, 3: output of slice with plane perpendicular to this direction'
2
With a value of 0 the output is suppressed.
A value of 1, 2, 3 indiciates the direction of the normal to the output plane:
for instance, in a local 3D "box-in-a-star" model with gravity along direction 3 a value
of 3 gives a horizontal plane in the middel of the model (useful only in special cases)
whereas a value of 2 (or 1) gives a vertical slice with a horizontal and the
vertical axis - useful for movies of 2D slices.
The grid index of the slice cannot be specified.
7.1.21.5 integer outdim_chu1
The dimension of an additional output chunk (1) written into a separate file can be specified
with this parameter (a 2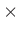 3 integer array).
The output of a horizontal slice at the 20th layer from the bottom
can be requested with:
3 integer array).
The output of a horizontal slice at the 20th layer from the bottom
can be requested with:
integer outdim_chu1 d=(1:2,1:3) f=I5 b=4 p=6 n='Chunk 1 dimension' u=1 &
c0='0: start from first, 9999: end with last'
0 9999 0 9999 20 20
The index ranges go from 1 to the number of elements in that dimension.
Specifying a lower first or a larger last dimension (as in the example),
means that all elements will be taken.
The output sampling rate is the same a for mean files.
Attention: a high sampling frequency of large chunks can produce large
files very quickly.
7.1.21.6 integer outdim_chu2
The dimension of another output chunk 2 written into a separate file can be specified
with this parameter, analogously to integer outdim_chu1 as e.g., in
integer outdim_chu2 d=(1:2,1:3) f=I5 b=4 p=6 n='Chunk 2 dimension' u=1 &
c0='0: start from first, 9999: end with last'
0 9999 100 100 0 9999
The dimension of another output chunk 2 written into a separate file can be specified
with this parameter, analogously to integer outdim_chu1 as e.g., in
integer outdim_chu3 d=(1:2,1:3) f=I5 b=4 p=6 n='Chunk 3 dimension' u=1 &
c0='0: start from first, 9999: end with last'
100 100 0 9999 0 9999
7.1.21.8 character infile_start
The filename of the initial model is specified e.g. with
character infile_start f=A80 b=80 n='File name of start model'
rhd.sta
Default is rhd.sta (for a parameter file used within a batch system).
Typical filenames are st35gm04n01_01.sta or gt57g44n20dz.end.
7.1.21.9 integer istep_in_start
The index number of the dataset in the start model file to be used can be specified, e.g. with
integer istep_in_start f=I4 b=4 n='Number of dataset to read as start model' &
u=1 c0='1: first dataset (default), 2: second dataset, ...'
1
7.1.21.10 character outfile_end
The file name for the final model can be specified with e.g.
character outfile_end f=A80 b=80 n='Output file name'
rhd.end
The default is rhd.end.
Leaving it empty means that no final model is written. This of course inhibits
follow-up simulations but can be useful to save time and disk space for some tests.
7.1.21.11 character outfile_full
The name of the file for the output of additional full models at regular intervals
(see Sect.8.1) can be given with e.g.
character outfile_full f=A80 b=80 n='Output file name'
rhd.full
Leaving it empty means that no file of this type is written.
7.1.21.12 character outfile_mean
The name of the file for the output of additional information (average stratification (1D),
mean fluxes (1D), surface intensities(2D)) at regular intervals (see Sect.8.3)
can be specified with e.g.
character outfile_mean f=A80 b=80 n='Output file name'
rhd.mean
Leaving it empty means that no file of this type is written.
7.1.21.13 character outfile_mcyl
The name of the file for the output of azimuthal averages (2D arrays for 3D models)
at regular intervals (see Sect.8.3)
can be specified with e.g.
character outfile_mcyl f=A80 b=80 n='Output file name'
rhd.mcyl
Leaving it empty means that no file of this type is written.
Only in the case of global models such data is computed.
It is particularly useful for rotating models.
7.1.21.14 character outfile_chu1
The name of the file for the output of an additional data chunk
at regular intervals (the same as for mean file)
can be specified with e.g.
character outfile_chu1 f=A80 b=80 n='Output file name for chunks'
rhd.chu1
The UIO format is the same as specified for mean files.
Leaving the name empty means that no file of this type is written.
7.1.21.15 character outfile_chu2
The name of the file for the output of an additional data chunk 2
can be specified with this parameter analogously to character outfile_chu1.
The name of the file for the output of an additional data chunk 3
can be specified with this parameter analogously to character outfile_chu1.
The format (see Sect.6.2.3.1) of the final model files
can be chosen e.g. with
character outform_end f=A80 b=80 n='Output file format' &
c0='formatted/unformatted'
unformatted
Allowed values are
unformatted: (default) fast compact (possibly machine-dependent) output:
strongly recommended
formatted: slow (machine-independent) output, big files
The conversion type (see Sect.6.2.3.1) of the final model files
can be specified e.g. with
character outconv_end f=A80 b=80 n='Output file conversion' &
c0='ieee_4/ieee_8/crayxmp_8/native'
ieee_4
The allowed values depend on the machine.
Leaving this field empty means that the default is chosen that is build into the local UIO module.
If the type ieee_4 is supported (which is always the case, so far) it should be chosen.
The format (see Sect.6.2.3.1) of the full model files
can be chosen e.g. with
character outform_full f=A80 b=80 n='Output file format' &
c0='formatted/unformatted'
unformatted
Allowed values are
unformatted: (default) fast compact (possibly machine-dependent) output:
strongly recommended
formatted: slow (machine-independent) output, big files
The conversion type (see Sect.6.2.3.1) of the full model files
can be specified e.g. with
character outconv_full f=A80 b=80 n='Output file conversion' &
c0='ieee_4/ieee_8/crayxmp_8/native'
ieee_4
The allowed values depend on the machine.
Leaving this field empty means that the default is chosen that is build into the local UIO module.
If the type ieee_4 is supported (which is always the case, so far) it should be chosen.
The format (see Sect.6.2.3.1) of the additional data files
can be chosen e.g. with
character outform_mean f=A80 b=80 n='Output file format' &
c0='formatted/unformatted'
unformatted
Allowed values are
unformatted: (default) fast compact (possibly machine-dependent) output:
strongly recommended
formatted: slow (machine-independent) output, big files
The conversion type (see Sect.6.2.3.1) of the additional data files
can be specified e.g. with
character outconv_mean f=A80 b=80 n='Output file conversion' &
c0='ieee_4/ieee_8/crayxmp_8/native'
ieee_4
The allowed values depend on the machine.
Leaving this field empty means that the default is chosen that is build into the local UIO module.
If the type ieee_4 is supported (which is always the case, so far) it should be chosen.
%




Next: 7.1.22 Scale and test
Up: 7.1 Parameter file: rhd.par
Previous: 7.1.20 Time-step control
Contents
Index